Learning to Prove Theorems by Learning to Generate Theorems
1.论文信息
作者: Mingzhe Wang, Jia Deng
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.07019 Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020
代码: https://github.com/princeton-vl/MetaGen
在这篇论文的正文还没有被我研(liu)读(lan)时,吸引我的点就有三个:
1)标题就很有吸引力有木有! 定理的生成意味着定理的证明,多多少少有些自我指涉的意味,进一步引起极大的兴趣去看一下这是如何做到的。论给论文起个好名字的重要性:-)
2)paperswithcode网站中Automated Theorem Proving分类下的简介就是来自于这篇论文1
3)论文的两位作者都来自于普林斯顿大学,而历史上第一个可运行的定理证明程序所用的机器就是普林斯顿高等研究院的电子管计算机“大强尼”(JOHNNIAC)1,可以说是在自动定理证明领域是根正苗红,莫名让人心生敬畏,respect
2.论文摘要与简介
自动定理证明可以归结为(boils down to)一个搜索问题——找到一个可以生成有效证明的符号操作系列,基础挑战在于搜索空间爆炸,特别针对本身就带有冗长证明和繁杂知识库。对定理的顺利证明来讲特别重要的是能找到可以引导证明器下一步该怎么做的有效启发方法,而深度学习在学习这样的搜索启发方法是大有可为的。之前的工作中以人写的定理-证明数据作为输入来训练网络模仿学习,但依赖于人写的数据有可用性和可扩展性的限制。本文提出用合成数据训练定理证明器,基本思想是构建一个生成器以自动合成新定理和证明数据,来增强人写数据进而训练证明器。
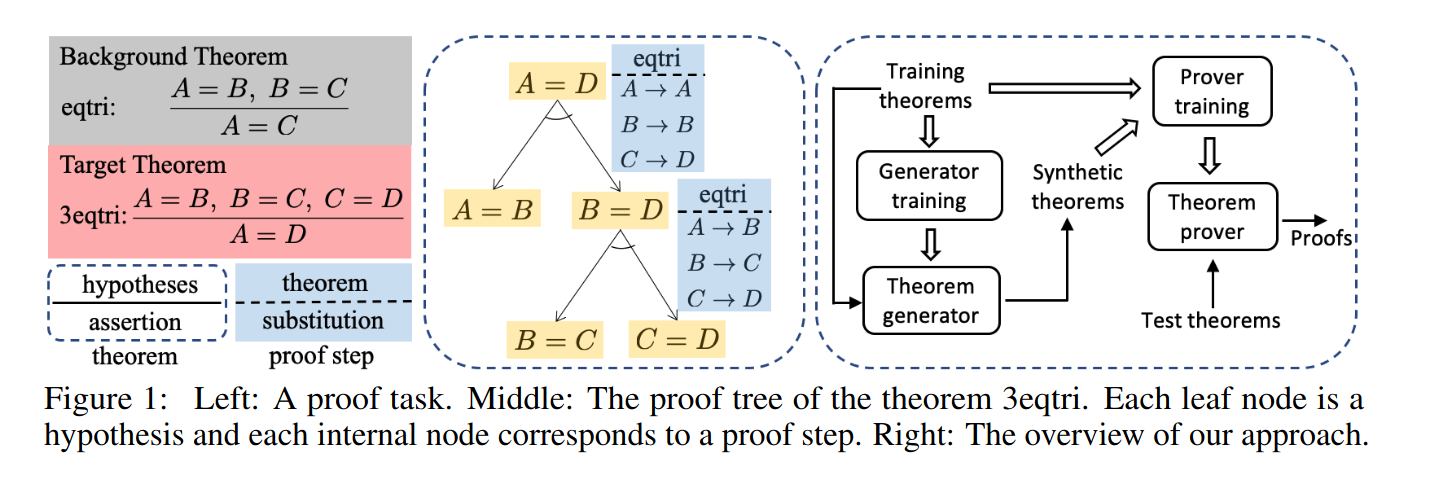
通过在已有的定理和证明中重复应用推断规则并组合证明来形成新的定理证明,生成器只需要按照自己的选择生成新定理,而证明器需要为了一个特定的目标定理找到证明。本文中假设生成的数据与人写数据越像就对训练模型越有用,如果人写数据只有定理没有证明就让强化学习来让生成器采取行动合成与人写定理相似的定理。与GAN类似,为了量化合成定理与人写定理的相似性,本文训练判别器来从合成定理中去分辨哪个是人写的。(防止打脸的谨慎谦虚写法:To the best of our knowledge) 本文提出的神经定理生成器MetaGen是第一个神经生成器用于定理证明的合成训练数据。
3.相关工作
1)Automated theorem proving
All of these methods are orthogonal to our approach because all of their provers are learned from human-written training data, whereas our prover is trained from human data augmented with synthetic data. Our contribution is on the generation of synthetic data and using such data to train a prover. Our reinforcement learning task is much easier because the reward is continuous and there are many ways to generate theorems similar to human-written ones.
2)Synthetic theorem generation
The main difference of our approach is that our generator is optimized through learning, as opposed to random generation. our approach synthesizes both new theorems and new proofs which could cover a much larger space of possible derivations than the proofs of existing human theorems.
we generate entirely new theorems and new proofs that are not part of any existing proofs
each of our synthetic theorem is guaranteed to be correct and its proof is automatically available.
3)Automatic goal generation by self-play
We pursue similar ideas in the new context of theorem proving by learning to generate synthetic theorems to train the prover. Also of note is that we have no adversarial self-play. The goal of the generator is to discover novel theorems similar to human-written ones, not to beat the prover. our generator and prover execute different tasks,and are co-operative. In addition, their game remains a theoretical proposal without any empirical validation, whereas we have performed experiments on large-scale data.
4.本文工作
1)Generator
We propose MetaGen, a neural generator that performs forward reasoning to synthesize theorems. It takes a set of training proof tasks as input and outputs a set of synthetic theorems. These synthetic theorems are then combined with original training proof tasks to train the theorem prover
2)Prover
We use Holophrasm as our theorem prover and augment its training with synthetic data. Given a proof task, Holophrasm conducts backward reasoning to prove the target theorem
3)Applicability to other formal systems
we instantiate and validate our approach on a single formal system, but our approach is applicable to other formal systems such as HOL Light, Coq and Isabelle.
5.实验结果
在两个Metamath知识库中进行实验: iset.mm,set.mm
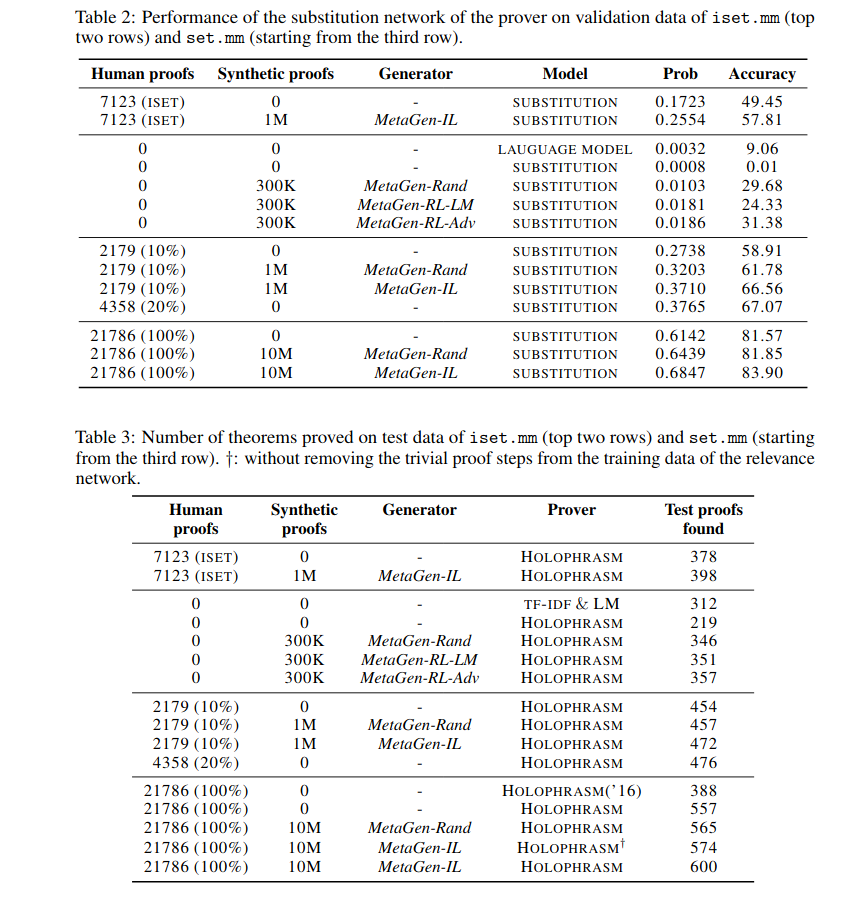
1)Relevance network of prover
We evaluate how synthetic data can improve the relevance networkof Holophrasm. The relevance network assigns a score to each candidate background theorem.
2)Substitution network of prover
We evaluate how synthetic data can improve the substitution network of Holophrasm. The substitution network predicts the probability of each token at each position under teacher forcing. In all settings, synthetic data brings significant improvement. The best performance is achieved with our trained generators.
3)Prover
the performance of the prover shares the same pattern as the relevance and substitution network. On both iset.mm and set.mm, the provers trained on synthetic data consistently prove more theorems than the provers trained on human proofs only.
the provers trained with learnable generators perform better than the provers trained with MetaGen-Rand.
6.结论
为了训练定理证明器(theorem prover),本文提出了一个可以自动合成定理和证明的神经生成器(neural generator),在真实世界任务实验中,用本文方法合成的数据有助于提高定理生成器,并在Metamath的自动定理证明中领先现有的SOTA.多说一句,自动定理证明在安全攸关应用(safety-critical applications)中特别重要,比如在自动驾驶的软件中。
参考:
- [2] 尼克.人工智能简史[M].人民邮电出版社,2017,11.