Neural Machine Translation: A Review of Methods, Resources, and Tools
1.论文信息
作者: Zhixing Tan, Shuo Wang, Zonghan Yang, Gang Chen, Xuancheng Huang, Maosong Sun, Yang Liu
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15515
这是清华大学计算机系与智能产业研究院的机器翻译研究团队发表的关于神经机器翻译技术的最新综述论文1
清华大学智能产业研究院(Institute for AI Industry Research, Tsinghua University,英文简称AIR)是面向第四次工业革命的国际化、智能化、产业化的应用研究机构。AIR的使命是利用人工智能技术赋能产业升级、推动社会进步。通过大学与企业创新双引擎,突破人工智能核心技术,培养智能产业领军人才,推动智能产业跨越式发展。2
2.论文摘要与简介
本篇综述摘要写得极其简洁优雅,一点废话都没有,值得学习,见贤思齐。
一共五句话:
1)大背景: 机器翻译是自然语言处理中重要的子领域(ps:此句后面加修饰语做个定义)
Machine translation (MT) is an important sub-field of natural language processing that aims to translate natural languages using computers.
2)小背景: 近年来端到端神经机器翻译成就非凡
In recent years, end-to-end neural machine translation (NMT) has achieved great success and has become the new mainstream method in practical MT systems
3)本文首先提供NMT方法的综观视角,并重点关注有关架构、解码和数据增强的方法
In this article, we first provide a broad review of the methods for NMT and focus on methods relating to architectures, decoding, and data augmentation
4)其次总结有用的资源和工具(ps:这句加限定对科研工作者有用以求严谨,对于开发落地者来说也许并不实用)
Then we summarize the resources and tools that are useful for researchers.
5)最后讨论可能的未来研究方向
Finally, we conclude with a discussion of possible future research directions.
引言部分提到NMT碾压以前机器翻译方法的地方在哪(Neural machine translation is a radical departure from previous machine translation approaches):
On the one hand, NMT employs continuous representations instead of discrete symbolic representations in SMT. On the other hand, NMT uses a single large neural network to model the entire translation process, freeing the need for excessive feature engineering.
本文希望站在过去研究的肩膀上可以获得一些未来NMT的启发:
We hope that by tracing the origins and evolution of NMT, we can stand on the shoulder of past studies, and gain insights into the future of NMT.
3.方法
We strive to answer the three basic questions of NMT:
Modeling
How to design neural networks to model the conditional distribution?
Inference
Given a source input, how to generate a translation sentence from the NMT model?
Learning
How to effectively learn the parameters of NMT from data?
1)Overview of NMT
Modeling
In this article, we focus on sentence-level translation. Besides, we also assumethe input and output sentences are sequences. Thus the NMT model can be viewed as a sequence-to-sequence model.
Inference
However, due to the intractably large search space, it is impractical to find the translation with the highest probability. Therefore, NMT typically uses local search algorithms such as greedy search or beam search to find a local best translation.
Training of NMT Models
In practice, instead of plain SGD optimizer, adaptive learning rate optimizers such as Adam are found to greatly reduce the training time.
2)Architectures
Evolution of NMT Architectures
However, it is found that the performance of this approach degrades as the length of the input sentence increases.Two explanations can account for this phenomenon:
(1)The fixed-length representations have become the bottle-neck during the encoding process for long sentences.As the encoder is forced to compress the entire source sentence into a set of fixed-length vectors, some important information may be lost in this process
(2)The longest path between the source words and target words is O(S+T), and it is challenging for neural networks to learn long-term dependencies. Sutskeveret al. found that reverse the source sentence can significantly improve the performance of the fixed-length approach.By reversing the source sentence, the paths between the beginning words of source and target sentences are reduced, thus the optimization problem becomes easier
Due to these limitations, later NMT architectures switch to variable-length source representations, where the length of source representations depends on the length of the source sentence.
Attention Mechanism
In practice, the dot-product attention is much faster than the additive attention. However, the dot-product attention is found to be less stable than the additive attention when d is large.
The attention mechanism is usually used as a part of the decoder network. Another type of attention network called self-attention network, is widely used in both the encoder and decoder of NMT.
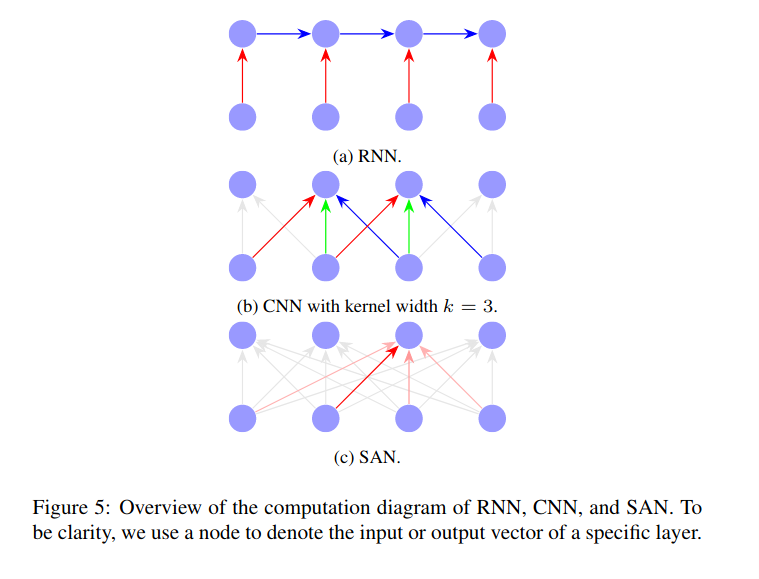
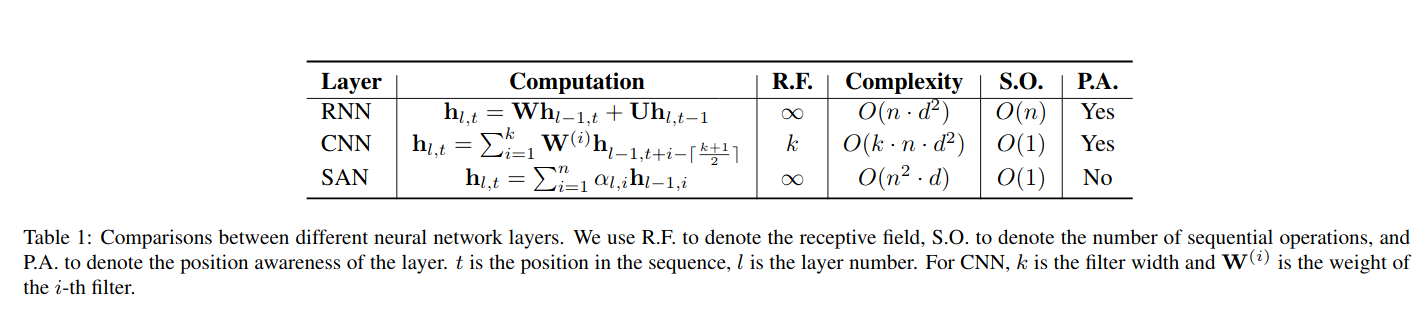
RNNs, CNNs, and SANs
There are several aspects we need to take into considerations for building an encoder and decoder:
1.Receptive field.
We hope each output produced by the encoder and decoder can potentially encode arbitrary information in the input sequence.
2.Computational complexity.
It is desirable to a use network with lower computational complexity.
3.Sequential operations.
Too many sequential operations preclude the parallel computation within the sequence.
4.Position awareness.
The network should distinguish the ordering presents in the sequence.
Bidirectional Inference and Non-autoregressive NMT
The bidirectional inference is an approach to simultaneously generating translation with both L2R and R2L decoders. In addition to auto-regressive approaches where each output word on previously generated outputs, non-autoregressive NMTs avoids this auto-regressive property and produces outputs in parallel,allowing much lower latency during inference
Alternative Training Objectives
Despite the remarkable success, Ranzato et al. indicate two drawbacks of MLE for NMT. First, NMT models are not exposed to their errors during training, which is referred to as the exposure bias problem. Second, MLE is defined at word-level rather than sentence-level. Due to these limitations,researchers have investigated several alternative objectives.
Using Monolingual Data and Unsupervised NMT
One way is called shallow fusion,which uses a language model during decoding to rescore the n-base list. Another way is called deep fusion, which combines the decoder and language model with a controller mechanism.However, the improvements of these approaches are limited.
Another way to use target-side monolingual data is called Back-translation(BT). BT can make use of target-side monolingual data without changing the architecture of NMT.
Besides target-side monolingual data, source-side monolingual data are also important resources to improve the translation quality of semi-supervised neural machine translation.
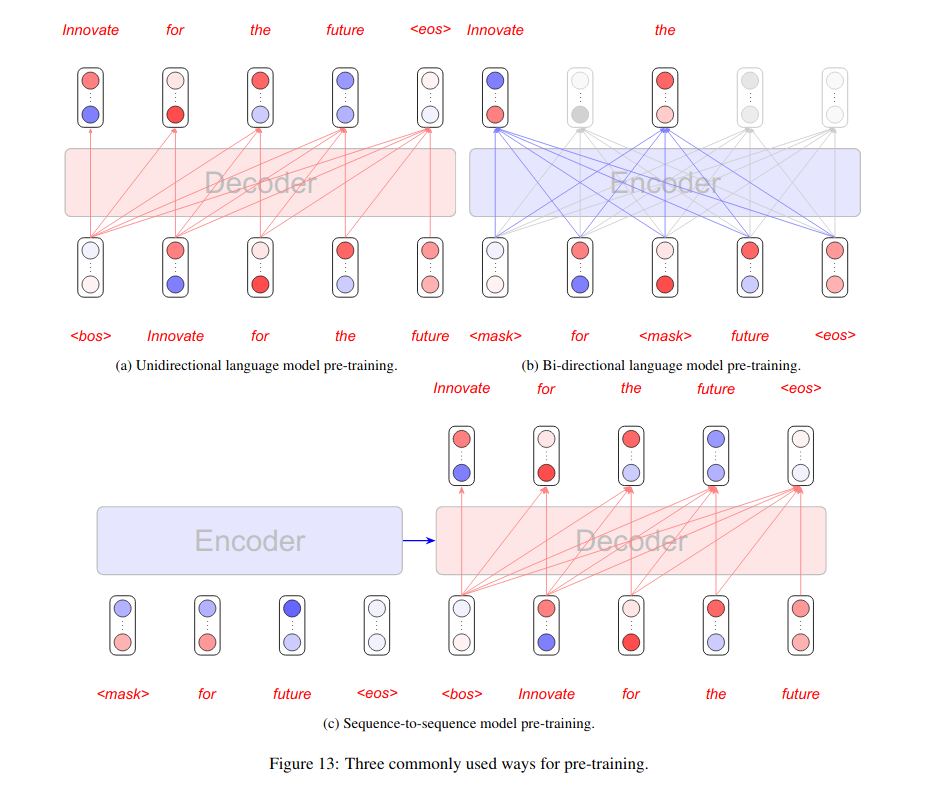
Pre-training is an alternative way to utilize monolingual datafor NMT, which is shown to be beneficial by further combining with back-translation in the supervised and unsupervised NMT scenario
Unsupervised neural machine translation aims to obtain a translation model without using parallel data. Apparently, unsupervised machine translation is much more difficult than the supervised and semi-supervised settings.
Open Vocabulary
Although word-level NMT is unable to translate out-of-vocabulary words, character-level NMT do not have this problem. By splitting words into characters, the vocabulary size is much smaller and every rare word can be represented.
Prior Knowledge Integration
One line of studies focus on inducing lexical knowledge into NMT models.
Another line of studies directly model the target-side syntactic structure
Interpretability and Robustness
All internal information in NMT is represented as high-dimensional real-valued vectors or matrices. Therefore, it is challenging to associate these hidden states with language structures. The lack of interpretability has made it very difficult for researchers to understand the translation process of NMT models.
With small perturbations in source inputs (also referred to as adversarial examples), the translations of NMT models may lead to significant erroneous changes.The lack of robustness of NMT limits its application on tasks that require robust performance on noisy inputs. Therefore, improving the robustness of NMT has gained increasing attention in the NMT community.
4.资源
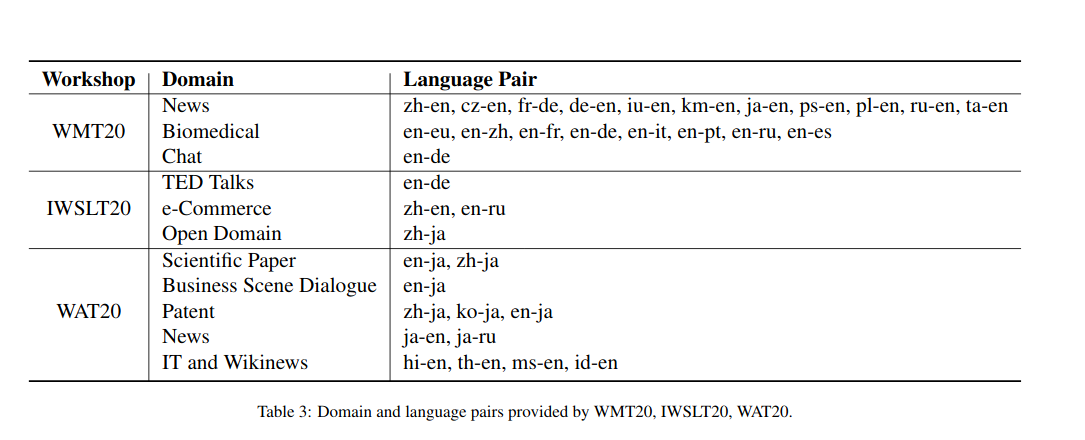
Parallel Data
Monolingual Data
Wikipedia provides database dump
5.工具
Open-source NMT Toolkits
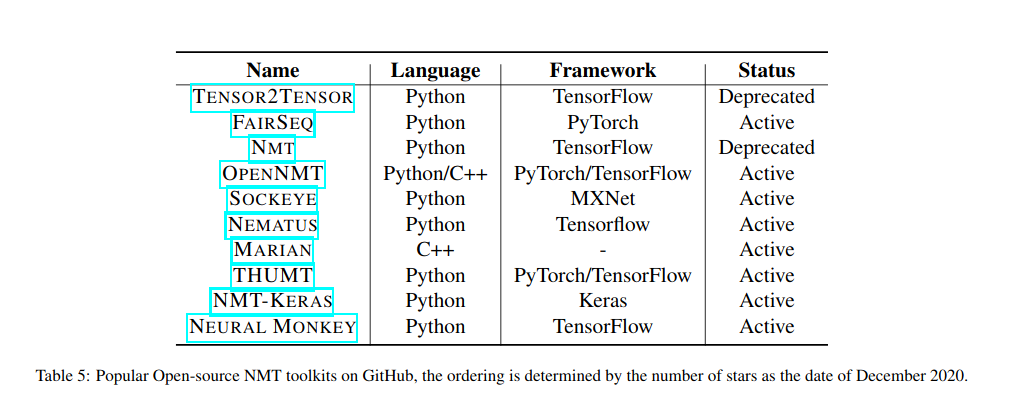
Tools for Evaluation and Analysis
Other Tools
6.结论
Neural machine translation has become the dominant approach to machine translation in both research and practice.This article reviewed the widely used methods in NMT, including modeling, decoding, data augmentation, interpretation, as well as evaluation. We then summarize the resources and tools that are useful for NMT research
Despite the great success achieved by NMT, there are still many problems to be explored. We list some important and challenging problems for NMT as follows:
Understanding NMT
Although there are many attempts to analyze and interpret NMT, our understandings about NMT are still limited. Understanding how and why NMT produces its translation result is important to figure out the bottleneck and weakness of NMT models.
Designing better architectures
Designing a new architecture that better than Transformer is beneficial for both NMT research and production. Furthermore, designing a new architecture that balances translation performance and computational complexity is also important.
Making full use of monolingual data
Monolingual dataare valuable resources.Despite the remarkable progress,we believe that there is still much room for NMT to make use of abundant monolingual data.
Integrating prior knowledge
Incorporating human knowledge into NMT is also an important problem. Although there is some progress, the results are far from satisfactory. How to convert discrete and continuous representations into each other is a problem of NMT that needs further exploration.
参考:
- [2] 我们是清华大学智能产业研究院