NaturalProofs: Mathematical Theorem Proving in Natural Language
1.论文信息
作者: Sean Welleck, Jiacheng Liu, Ronan Le Bras, Hannaneh Hajishirzi, Yejin Choi, Kyunghyun Cho
机构: 华盛顿大学,艾伦人工智能研究院,纽约大学
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01112
代码&数据集: https://github.com/wellecks/naturalproofs
本文是自然语言预训练的数学领域实践,最终发现预训练语言模型是一个很好的解决数学任务的起始点1
有种说法是数学是一种语言,那如此一来用预训练语言模型做数学定理证明是自然而然的事情,不过这个说法有些许争议,”Mathematics is a written form of communication”2
2.论文摘要与简介
we develop NATURALPROOFS, a large-scale dataset of mathematical statements and their proofs, written in natural mathematical language.Using NATURALPROOFS, we propose a mathematical reference retrieval task that tests a system’s ability to determine the key results that appear in a proof.
We expect that mastery of this task requires natural language ability,analogical and logical reasoning, knowledge retrieval, and mathematical domain knowledge. A machine learning system that performs well on this task could provide guidance to mathematicians or researchers while proving new theorems, aid in developing novel exercises, and offer hints to students that are stuck on how to proceed with a problem.
We find that language pretraining is an effective initialization for our mathematical task, and that the models leverage both the textual information in the title and the mathematical contents of each statement. However, in absolute terms their performance leaves substantial room for improvement.NATURALPROOFS opens many possibilities for developing and evaluating machine learning methods on challenging mathematical tasks.
3.相关工作
1)Machine learning for formalized mathematics.
Wang et al. (2020) explore translating between informal and formal mathematics, including via a dataset based on ProofWiki, on which NATURALPROOFS is also based,though their dataset is not made available.
2)Mathematics and language benchmarks.
NATURAL-PROOFS focuses on theorem proving rather than calculation,which we hypothesize evaluates different capabilities, and may prove useful in bridging formal and informal settings.
3)Large-scale neural language models.
Recent work suggests that these models store knowledge in their parameters (Petroniet al., 2020), are capable of reasoning in mathematical (Rabeet al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021) and language (Clark et al., 2020;Tafjord et al., 2020) domains, and are effective for information retrieval tasks (Nogueira & Cho, 2020; Nogueira dosSantos et al., 2020).These advances motivate our work, which explores mathematical reasoning in natural language with large-scale language models through a retrieval task.
4.数据集
NATURALPROOFS consists of roughly 20,000 theorem statements and proofs, 12,500 definitions, and 1,000 additional pages (e.g. axioms, corollaries) derived from ProofWiki,an online compendium of mathematical proofs written by a community of contributors.
5.检索任务
In this section, we propose a mathematical reference retrieval task: given a theorem x, retrieve the set of references y that occur in the theorem’s proof.
6.实验
The aim of our experiments is to benchmark existing methods developed in natural language processing on the NATURALPROOFS mathematical reference retrieval task.
By varying the parameterization of fθ and gθ, which encode the statement and reference, respectively, we can evaluate the performance of commonly used natural language processing methods on the task of reference retrieval.
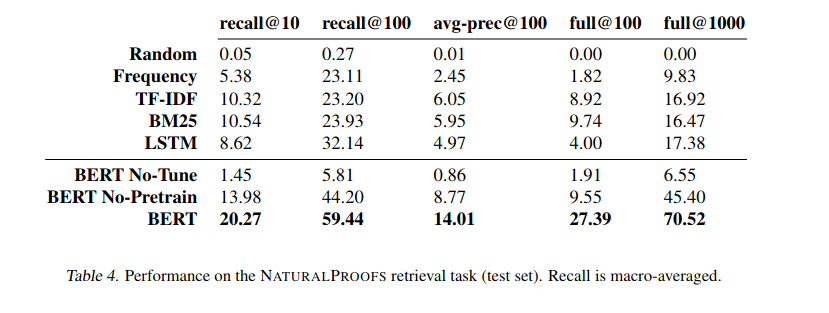
The results demonstrate that large-scale pretrained neural language models are effective for mathematical reference retrieval compared to previous alternatives. However, despite their strong relative performance, their absolute performance leaves a large amount of room for improvement.For instance, although each theorem contains on average eight true references, the BERT model fails to retrieve all of them in the top hundred roughly 75% of the time. To better understand the model’s strengths, weaknesses, and the factors that contribute to its performance, we perform several analyses beginning with a qualitative evaluation.
Future Directions
Using NATURALPROOFS to develop methods for evaluating generated mathematical content is an interesting direction for future work.
Finally,NATURALPROOFS provides a data schema for mathematical theorems, proofs, and references that is independent of the ProofWiki data used to the populate the dataset. With this schema in place, an exciting direction is leveraging other mathematical data sources for expanding the training set or deriving challenging evaluation sets.
7.结论
As a step in this direction, we develop NATURALPROOFS, a large-scale dataset for studying mathematical reasoning in natural language. We propose a retrieval task that represents a key step in real-world theorem proving: choosing the existing results that occur in the proof of a novel mathematical claim. Our experiments suggest that the task is tractable, yet challenging, for current large-scale neural sequence models.NATURALPROOFS opens many promising avenues for future research.